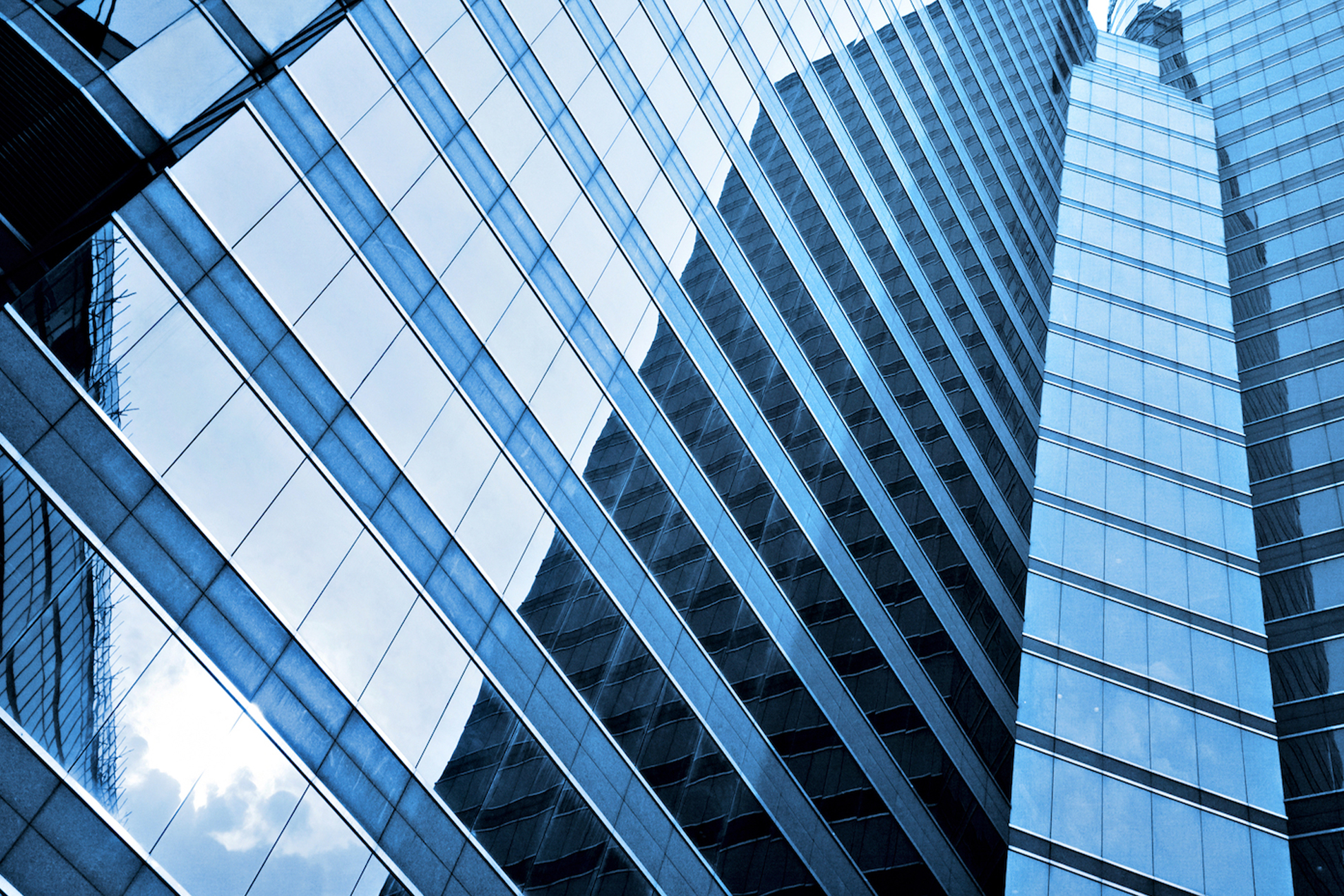
Laminated glass is a three-layered glass primarily used for safety, infrastructure, and construction. Determining how to cut laminated glass in your manufacturing facility depends on the features of your end product. What material is your interlayer made of? Do you require straight, curved, or custom cuts? The technical nature and demanding uses of laminated glass necessitate a tailored cutting solution that guarantees the reliable performance of your product for years to come.
What is Laminated Glass Used For?
Laminated glass is both transparent and reinforced, a unique combination of features that makes it ideal for a variety of applications. The material, depending on its specific makeup, can resist impact, dampen sound, filter UV radiation, and withstand heat. These characteristics offer numerous advantages, including:
- Safety: Laminated glass is impact-resistant, protecting buildings and vehicles from break-ins, bullets, and inclement weather. If an object does break the glass, the glass does not shatter because it’s attached to the interlayer material.
- Versatility: The many characteristics and configurations of laminated glass make it a versatile building material. Designers can use laminated glass in both flat and curved applications with varying opacity, as well as meet other application requirements.
- Clarity: Depending on the application, transparency and visual clarity remain just as important as other features of laminated glass. With the right interlayer material, laminated glass has little visual distortion.
Thanks to these advantages, engineers, architects, and other design professionals rely on laminated glass across industries. Laminated glass is used in architecture for windows, skylights, and walls. The material is also used in the automotive, aerospace, marine, and solar industries.
How is Laminated Glass Made?
Laminated glass is composed of multiple layers; usually, there is a single interlayer sandwiched between two layers of glass. Potential interlayer materials include, but are not limited to, PVB (polyvinyl butyral), SentryGlas™ Plus (SGP), EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate), and TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane). The three layers are first manufactured, cut, washed, and dried separately. The glass lamination process begins when the layers are assembled. Then, the vinyl or fabric interlayer is bonded to each piece of glass using the heat and pressure of an autoclave.
Types of Laminated Glass
SGP: SGP laminated glass is a sturdy option; this kind of interlayer boasts about 100 times the rigidity and five times the tear resistance as PVB materials. SGP is also vastly more water resistant, affording it both interior and exterior applications like balustrades, security glass, floors, stairs, and skylights. Due to these advantages, SGP is known to be significantly more expensive than most other kinds of laminated glass and cannot be combined with other interlayers for custom cuts.
PVB: PVB laminated glass is well-known for being highly transparent and flexible. Because PVB is very adhesive, affordable, and has some protective qualities against UV rays, it’s the primary interlayer option used by manufacturers in the industry. The most common uses include A-grade safety glass for interior residential and commercial windows, doors, balustrades, and glass partitioning. It should not be used in instances where the glass will have extended contact with moisture or water, as this can cause the glass to de-laminate.
EVA: EVA laminated glass is a common alternative to PVB since it offers high moisture resistance and can be used for internal and external applications. It also is more adherent than PVB, available in many colors and tints, and can be combined with fabrics, wire mesh, and other unconventional materials in the glass build-up process. Therefore, EVA is often used when decorative glass options are desired. However, EVA doesn’t have quite the same structural integrity as SGP and is not as cost-effective as PVB materials.
TPU: Combining clarity, adhesion, strength, and resilience, TPU laminated glass is considered one of the highest-quality options in the industry. It is often used for architectural and security glass applications, including automotive and marine, that require considerable impact resistance from hurricanes and other severe weather. Aside from impact, TPU is also extremely resistant to UV degradation and humidity. With so many crucial benefits and areas of application, TPU is one of the more expensive interlayer options when compared to its alternatives.
How to Cut Laminated Glass
The technical nature of laminated glass interlayers requires specialty cutting and material handling solutions.
The technical applications of laminated glass, from architecture to aerospace, necessitate high-quality and incredibly accurate cuts. Miscut interlayers can wreak havoc at each stage of the glass lamination process and have lasting effects on the quality of the end product. Inaccurate cuts can lead to delamination and weakness, which affect the reliability of your product.
Eastman customizes its cutting systems and accessories to a manufacturer’s specifications. Production facilities determining how best to cut laminated glass for industrial applications are no different. Our automated cutting machines cut laminated glass with the precision required in industrial applications. A computer-controlled cutter reduces labor costs, minimizes human error, and decreases material waste. Automated cutting equipment allows for a variety of straight, curved, and custom cuts.
Eastman tool heads can be fitted with two or three spindles, further increasing the versatility and productivity of the cutting machine. Our automated cutting machines can be configured with both drag and round knives based on the interlayer type and application. Cleanroom configurations are common when working with laminated glass components; Eastman offers various system options to meet these contaminant-free standards. Smooth, easy-to-clean yet durable urethane cutting surfaces help manufacturers achieve quality cuts and defect-free end products. Eastman also provides material handling solutions that keep direct contact with technical interlayers to a minimum and further reduce manual labor while increasing cutting efficiency.
To learn more about our industry-specific solutions for cutting laminated glass, check out our Laminated Glass Brochure.
Every Eastman cutting solution is paired with personalized technical service. Our expertise allows us to help manufacturers improve cutting room efficiencies and best determine how to cut laminated glass interlayers in their facilities. Contact our experienced technical team to find the right cutting products for your application.